Lecture 07
Data Visualization
2025-02-15
Data Visualization
ggplot
ggplot2is a library is based on the grammar of graphicsthe idea is you can build every graph from the same few components:
- a data set
- geom(s)
- a coordinate system
ggplot2provides a programmatic interface for specifying- what variables to plot
- how they are displayed
- general visual properties.
ggplot
Therefore, we only need minimal changes if the underlying data changes or if we decide to change our visual.
This helps create publication quality plots with minimal amounts of adjustments and tweaking.
ggplot likes data in the ‘long’ format: i.e., a column for every dimension, and a row for every observation. (more on this next week…)
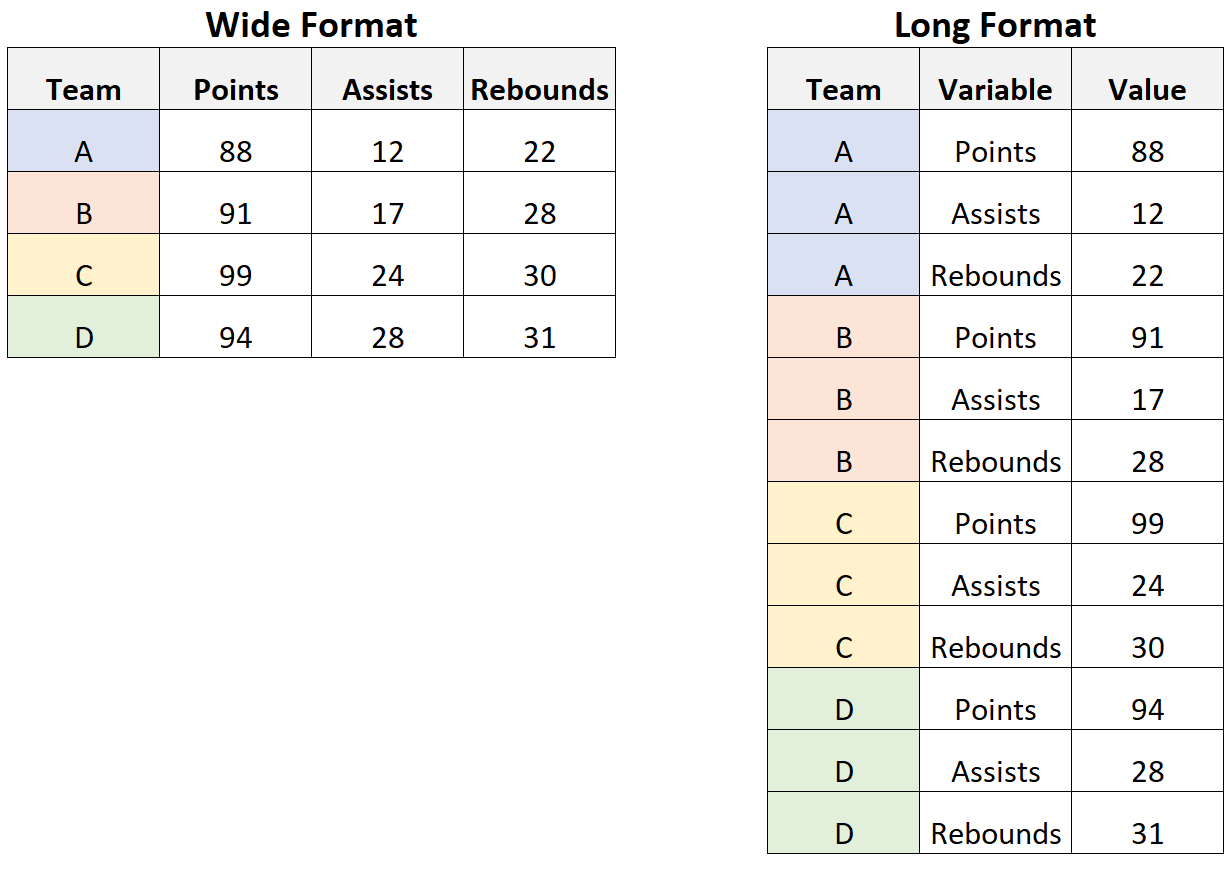
Components of a ggplot:
ggplot graphics are built step by step by adding new elements and layers
- Data
- Geometry (geom)
- Aesthetic mapping
- Theme
Elements of a plot are layered by iteratively adding elements
These can be added in a series of 5 steps:
- Setup
- Layers
- Labels
- Facets
- Themes
Example Data for today …
library(gapminder); library(dplyr);library(ggplot2)
(gm2007 = filter(gapminder, year == 2007))
#> # A tibble: 142 × 6
#> country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Afghanistan Asia 2007 43.8 31889923 975.
#> 2 Albania Europe 2007 76.4 3600523 5937.
#> 3 Algeria Africa 2007 72.3 33333216 6223.
#> 4 Angola Africa 2007 42.7 12420476 4797.
#> 5 Argentina Americas 2007 75.3 40301927 12779.
#> 6 Australia Oceania 2007 81.2 20434176 34435.
#> 7 Austria Europe 2007 79.8 8199783 36126.
#> 8 Bahrain Asia 2007 75.6 708573 29796.
#> 9 Bangladesh Asia 2007 64.1 150448339 1391.
#> 10 Belgium Europe 2007 79.4 10392226 33693.
#> # ℹ 132 more rows1. The Setup: canvas
1. The Setup: data
1. The Setup: Aesthetic Mappings
Aesthetic mappings describe how variables in the
dataare visualizedDenoted by the
aesargumentCan be set in ggplot() and/or in individual layers.
Aesthetic mappings in the ggplot() call, can be seen by all geom layers.
The X and Y axis of the plot as well colors, sizes, shapes, fills are all aesthetic.
If you want to have an aesthetic fixed (that is not vary based on a variable) you need to specify it outside the aes()
2. Layers
The
+sign is used to add layers to aggplotsetupLayers can define geometries, compute summary statistics, define what scales to use, or even change styles.
In general a plot construction will look like this:
2. Layers: Geometry
Many layers in
ggplot2are called ‘geoms’.geomsare the geometric objects (points, lines, bars, etc.) that can be placed on a graph to visualize theX-Y mappingof the inputdata/aesThey are called using functions that start with
geom_*.Examples include:
- points (
geom_point, for scatter plots, dot plots, etc) - lines (
geom_line, for time series, trend lines, etc) - boxplots (
geom_boxplot) - … and many more!
- points (
ls(pattern = '^geom_', env = as.environment('package:ggplot2'))
#> [1] "geom_abline" "geom_area" "geom_bar"
#> [4] "geom_bin_2d" "geom_bin2d" "geom_blank"
#> [7] "geom_boxplot" "geom_col" "geom_contour"
#> [10] "geom_contour_filled" "geom_count" "geom_crossbar"
#> [13] "geom_curve" "geom_density" "geom_density_2d"
#> [16] "geom_density_2d_filled" "geom_density2d" "geom_density2d_filled"
#> [19] "geom_dotplot" "geom_errorbar" "geom_errorbarh"
#> [22] "geom_freqpoly" "geom_function" "geom_hex"
#> [25] "geom_histogram" "geom_hline" "geom_jitter"
#> [28] "geom_label" "geom_line" "geom_linerange"
#> [31] "geom_map" "geom_path" "geom_point"
#> [34] "geom_pointrange" "geom_polygon" "geom_qq"
#> [37] "geom_qq_line" "geom_quantile" "geom_raster"
#> [40] "geom_rect" "geom_ribbon" "geom_rug"
#> [43] "geom_segment" "geom_sf" "geom_sf_label"
#> [46] "geom_sf_text" "geom_smooth" "geom_spoke"
#> [49] "geom_step" "geom_text" "geom_tile"
#> [52] "geom_violin" "geom_vline"2. Layers: Geometry
A plot must have at least one geom, but there is no maximum.
Adding geoms to a ggplot follows the pattern:
- Note again that the aesthetics placed in the
ggplotcall are the global parameters for the plot, and the aesthetics placed in eachgeomare specific to thatgeom.
A first geom_* …
A first geom_* …
2. Layers: Geometry
Like the set up, geoms can be modified with aesthetics (aes). Examples include:
- position (i.e., on the x and y axes)
- color (“outside” color)
- fill (“inside” color)
- shape
- line type
- size
. . .
Each geom accepts only a subset of these aesthetics
(refer to the geom help pages (e.g. ?geom_point) to see what mappings each geom accepts.

2. Layers: data.frame driven/fixed?
For our example…
For our example…
For our example…
For our example…
For our example…
3. Labels
Now that you have drawn the main parts of the graph. You might want to add labs that clarify what is being shown.
This can be done using the
labslayer.The most typical are:
title,x, andybut other options exist!
For our example…
For our example…
For our example…
For our example…
For our example…
For our example…
ggplot(data = gm2007, aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
geom_smooth(color = "black", size = .5) +
geom_hline(yintercept = mean(gm2007$lifeExp), color = "gray") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(gm2007$gdpPercap), color = "gray") +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population")4. Facets
In the previous chart, we showed a scatterplot for all countries plotted in the same chart. What if you want one chart for each continent?
Such separation is called
facetingfacet_wrap()takes in a formula as the argument.Formulas look like this
RHS ~ LHS(where RHS = right hand side, LHS = left hand side)
The item on the RHS corresponds to the column. The item on the LHS defines the rows.
In
facet_wrap, the scales of the X and Y axis are fixed to accommodate all points by default.This makes the comparison of values more meaningful because they would be in the same scale.
The scales can be made
freeby setting the argumentscales=free.
Facet Wrap…
Facet Wrap…
Facet Wrap…
Facet Wrap…
Facet Wrap…
Facet Wrap…
ggplot(data = gm2007, aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
geom_smooth(color = "black", size = .5) +
geom_hline(yintercept = mean(gm2007$lifeExp), color = "gray") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(gm2007$gdpPercap), color = "gray") +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population")Facet Wrap…
ggplot(data = gm2007, aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
geom_smooth(color = "black", size = .5) +
geom_hline(yintercept = mean(gm2007$lifeExp), color = "gray") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(gm2007$gdpPercap), color = "gray") +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
facet_wrap(~continent)Facet Wrap…
ggplot(data = gm2007, aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
geom_smooth(color = "black", size = .5) +
geom_hline(yintercept = mean(gm2007$lifeExp), color = "gray") +
geom_vline(xintercept = mean(gm2007$gdpPercap), color = "gray") +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
facet_wrap(~continent) +
facet_wrap(~continent, scales = "free")Facet Grids…
#> # A tibble: 1,704 × 6
#> country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.
#> 2 Afghanistan Asia 1957 30.3 9240934 821.
#> 3 Afghanistan Asia 1962 32.0 10267083 853.
#> 4 Afghanistan Asia 1967 34.0 11537966 836.
#> 5 Afghanistan Asia 1972 36.1 13079460 740.
#> 6 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786.
#> 7 Afghanistan Asia 1982 39.9 12881816 978.
#> 8 Afghanistan Asia 1987 40.8 13867957 852.
#> 9 Afghanistan Asia 1992 41.7 16317921 649.
#> 10 Afghanistan Asia 1997 41.8 22227415 635.
#> # ℹ 1,694 more rowsFacet Grids…
#> # A tibble: 426 × 6
#> country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Afghanistan Asia 1952 28.8 8425333 779.
#> 2 Afghanistan Asia 1977 38.4 14880372 786.
#> 3 Afghanistan Asia 2007 43.8 31889923 975.
#> 4 Albania Europe 1952 55.2 1282697 1601.
#> 5 Albania Europe 1977 68.9 2509048 3533.
#> 6 Albania Europe 2007 76.4 3600523 5937.
#> 7 Algeria Africa 1952 43.1 9279525 2449.
#> 8 Algeria Africa 1977 58.0 17152804 4910.
#> 9 Algeria Africa 2007 72.3 33333216 6223.
#> 10 Angola Africa 1952 30.0 4232095 3521.
#> # ℹ 416 more rowsFacet Grids…
Facet Grids…
Facet Grids…
gapminder %>%
filter(year %in% c(1952, 1977, 2007)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population")Facet Grids…
gapminder %>%
filter(year %in% c(1952, 1977, 2007)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
facet_wrap(year~continent)Facet Grids…
gapminder %>%
filter(year %in% c(1952, 1977, 2007)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
facet_wrap(year~continent) +
facet_grid(year~continent)Facet Grids…
gapminder %>%
filter(year %in% c(1952, 1977, 2007)) %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
facet_wrap(year~continent) +
facet_grid(year~continent) +
facet_grid(continent~year)Grids vs Wrap
facet_wrap(): Used for one faceting variable (or two), automatically wraps facets into rows and columns for a flexible layout.facet_grid(): Used for two faceting variables, arranges plots in a strict row-column grid.
Layout Difference: facet_wrap() optimizes space, while facet_grid() maintains a fixed structure.
Use Case: Use facet_wrap() for many categories without hierarchy; use facet_grid() for structured relationships between two variables.
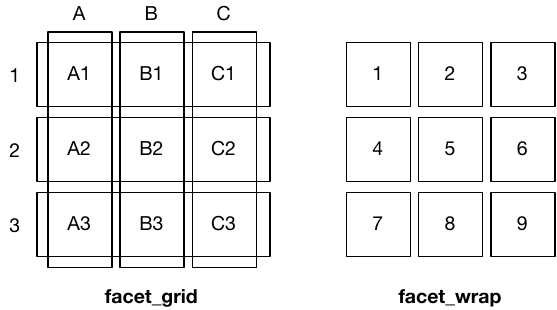
5. Theme
Great! Now we just need to polish our plots…
ggplot offers a themeing system:
elementsspecify the non-data elements that you can control. For example,
plot.titlecontrols the appearance of the plot title;axis.ticks.xcontrols the ticks on the x axis;legend.key.height, controls the height of the keys in the legend.
- Each
elementis associated with an element function, which describes the visual properties. For example,
element_text()sets the font size, color and face of text elements likeplot.title.
- The
theme()function which allows you to override default elements:
- For example
theme(plot.title = element_text(color = "red")).
Built in themes
Wow! That’s a lot :) Fortunately, ggplot comes with many default themes that set all of the theme elements to values designed to work together harmoniously.
#> [1] "theme_bw" "theme_classic" "theme_dark" "theme_get"
#> [5] "theme_gray" "theme_grey" "theme_light" "theme_linedraw"
#> [9] "theme_minimal" "theme_replace" "theme_set" "theme_test"
#> [13] "theme_update" "theme_void"theme_bw()
- All themes are )functions_ that “precann” a specified set of rules:
theme_bw
#> function (base_size = 11, base_family = "", base_line_size = base_size/22,
#> base_rect_size = base_size/22)
#> {
#> theme_grey(base_size = base_size, base_family = base_family,
#> base_line_size = base_line_size, base_rect_size = base_rect_size) %+replace%
#> theme(panel.background = element_rect(fill = "white",
#> colour = NA), panel.border = element_rect(fill = NA,
#> colour = "grey20"), panel.grid = element_line(colour = "grey92"),
#> panel.grid.minor = element_line(linewidth = rel(0.5)),
#> strip.background = element_rect(fill = "grey85",
#> colour = "grey20"), complete = TRUE)
#> }
#> <bytecode: 0x130765670>
#> <environment: namespace:ggplot2>Built in Themes…
#> # A tibble: 142 × 6
#> country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Afghanistan Asia 2007 43.8 31889923 975.
#> 2 Albania Europe 2007 76.4 3600523 5937.
#> 3 Algeria Africa 2007 72.3 33333216 6223.
#> 4 Angola Africa 2007 42.7 12420476 4797.
#> 5 Argentina Americas 2007 75.3 40301927 12779.
#> 6 Australia Oceania 2007 81.2 20434176 34435.
#> 7 Austria Europe 2007 79.8 8199783 36126.
#> 8 Bahrain Asia 2007 75.6 708573 29796.
#> 9 Bangladesh Asia 2007 64.1 150448339 1391.
#> 10 Belgium Europe 2007 79.4 10392226 33693.
#> # ℹ 132 more rowsBuilt in Themes…
Built in Themes…
Built in Themes…
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population")Built in Themes…
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
theme_bw()Built in Themes…
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
theme_bw() +
theme_dark()Built in Themes…
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
theme_bw() +
theme_dark() +
theme_gray()Built in Themes…
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
theme_bw() +
theme_dark() +
theme_gray() +
theme_minimal()Built in Themes…
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
theme_bw() +
theme_dark() +
theme_gray() +
theme_minimal() +
theme_light()ggtheme package…
ggtheme package…
#> # A tibble: 142 × 6
#> country continent year lifeExp pop gdpPercap
#> <fct> <fct> <int> <dbl> <int> <dbl>
#> 1 Afghanistan Asia 2007 43.8 31889923 975.
#> 2 Albania Europe 2007 76.4 3600523 5937.
#> 3 Algeria Africa 2007 72.3 33333216 6223.
#> 4 Angola Africa 2007 42.7 12420476 4797.
#> 5 Argentina Americas 2007 75.3 40301927 12779.
#> 6 Australia Oceania 2007 81.2 20434176 34435.
#> 7 Austria Europe 2007 79.8 8199783 36126.
#> 8 Bahrain Asia 2007 75.6 708573 29796.
#> 9 Bangladesh Asia 2007 64.1 150448339 1391.
#> 10 Belgium Europe 2007 79.4 10392226 33693.
#> # ℹ 132 more rowsggtheme package…
ggtheme package…
ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population")ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
ggthemes::theme_stata()ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
ggthemes::theme_stata() +
ggthemes::theme_economist()ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
ggthemes::theme_stata() +
ggthemes::theme_economist() +
ggthemes::theme_economist_white()ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
ggthemes::theme_stata() +
ggthemes::theme_economist() +
ggthemes::theme_economist_white() +
ggthemes::theme_fivethirtyeight()ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
ggthemes::theme_stata() +
ggthemes::theme_economist() +
ggthemes::theme_economist_white() +
ggthemes::theme_fivethirtyeight() +
ggthemes::theme_gdocs()ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
ggthemes::theme_stata() +
ggthemes::theme_economist() +
ggthemes::theme_economist_white() +
ggthemes::theme_fivethirtyeight() +
ggthemes::theme_gdocs() +
ggthemes::theme_excel()ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
ggthemes::theme_stata() +
ggthemes::theme_economist() +
ggthemes::theme_economist_white() +
ggthemes::theme_fivethirtyeight() +
ggthemes::theme_gdocs() +
ggthemes::theme_excel() +
ggthemes::theme_wsj()ggtheme package…
library(ggthemes)
gm2007 %>%
ggplot(aes(x = gdpPercap, y = lifeExp)) +
geom_point(aes(color = continent, size = pop)) +
labs(title = "Per capita GDP versus life expectency in 2007",
x = "Per Capita GDP",
y = "Life Expectancy",
caption = "Based on Hans Rosling Plots",
subtitle = 'Data Source: Gapminder',
color = "",
size = "Population") +
ggthemes::theme_stata() +
ggthemes::theme_economist() +
ggthemes::theme_economist_white() +
ggthemes::theme_fivethirtyeight() +
ggthemes::theme_gdocs() +
ggthemes::theme_excel() +
ggthemes::theme_wsj() +
ggthemes::theme_hc()Saving a ggplot element…
- Remember that in R, we assign object to names. We have seen examples including values, data structures, and functions:
- ggplot outputs are also objects!
ggsave()
ggplotcomes with a functionggsave(), that write a gg object to a file path (with path, name, extension)
Assignment
In your ess-330-daily-exercises project…
- Make a new
Rdirectory (mkdirR from the parent directory) - Create a new R file called day-07.R (touch R/day-07.R)
- Open that file.
- This is an R script. Unlike Quarto it will not knit, but unlike the console, it will save and keep your code.
- In this file add your name, date, and the purpose of the script as comments (preceded by #)
- Now, read in the COVID-19 data from the URL like yesterday
Question 1
Make a faceted line plot (geom_line) of the 6** states with most cases. Your X axis should be the date and the y axis cases.**
We can break this task into 4 steps:
- Identify the six states with the most current cases (yesterdays assignment +
dplyr::pull) - Filter the raw data to those 6 states (hint:
%in%) - Set up a ggplot –> add layers –> add labels –> add a facet –> add a theme
- save the image to you
imgdirectory (hint:ggsave())
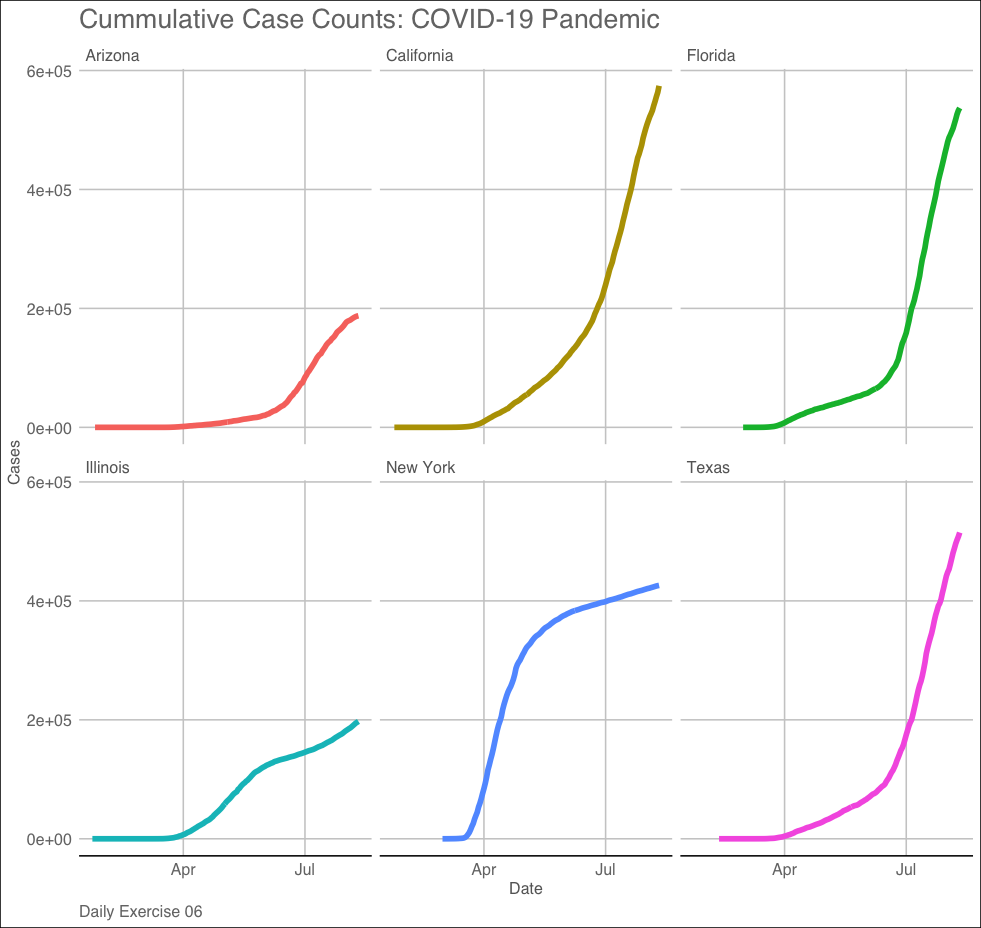
Question 2:
Make a column plot (
geom_col) of daily total cases in the USA. Your X axis should be the date and the y axis cases.
We can break this task into 3 steps:
- Identify the total cases each day in the whole country (hint:
group_by(date)) - Set up a ggplot –> add layers –> add labels –> add a theme
- Save the image to your
imgdirectory (hint:ggsave())
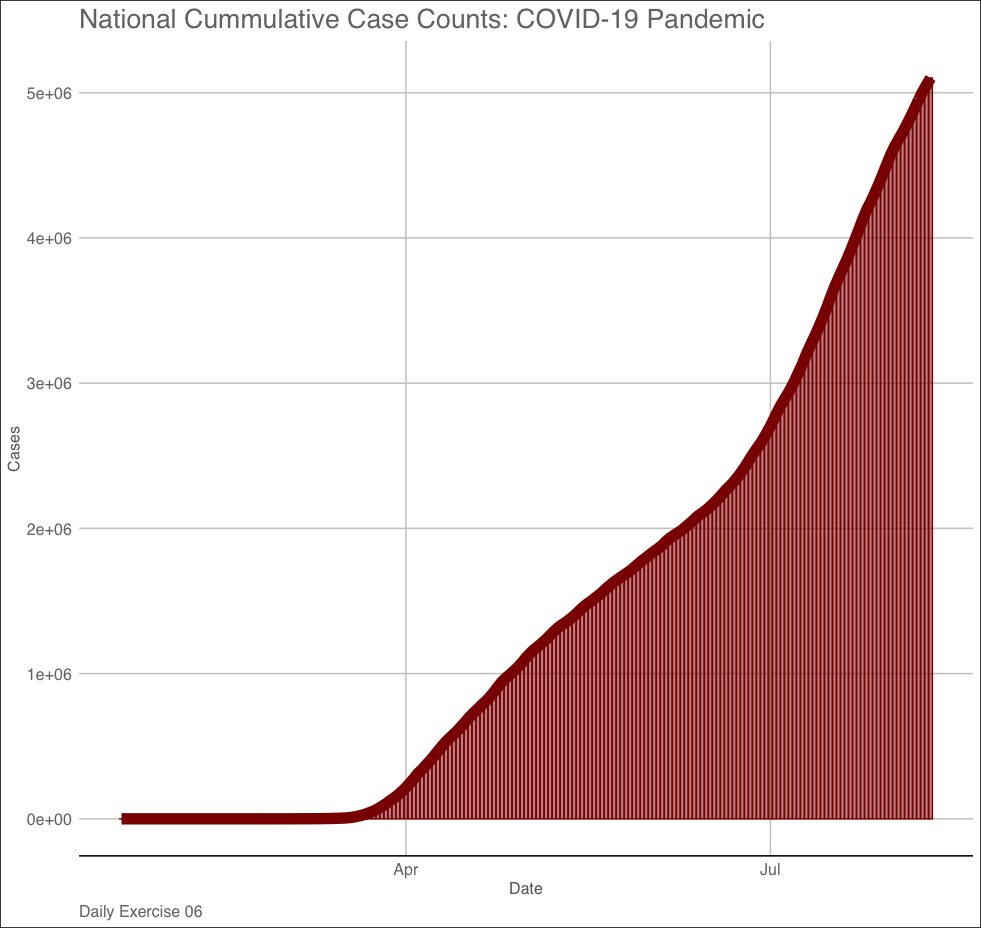
Submission:
Turn in your Rscript, and 2 images to the Canvas dropbox
